Comprehending Sugar Beet Vs Sugar Cane: a Deep Study Their Handling and Applications
The comparison between sugar beet and sugar cane discloses important distinctions in their processing and usage. Each plant has one-of-a-kind cultivation methods that influence its geographic circulation. Sugar beetroots are largely refined right into granulated sugar for various food products, while sugar cane is usually made use of in beverages. Recognizing these distinctions loses light on their roles in the food industry and their economic significance. Yet, the wider ramifications of their cultivation and processing require more expedition.
Introduction of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane
Sugar beet and sugar cane are 2 main resources of sucrose, each contributing substantially to the global sugar supply. Sugar beet is an origin veggie, typically harvested in cooler environments, while sugar cane is a high lawn that prospers in warmer exotic and subtropical areas. The handling of sugar beet entails washing, slicing, and extracting juice, followed by filtration and formation. On the other hand, sugar cane processing includes crushing the stalks to draw out juice, which is then made clear and focused into sugar crystals.
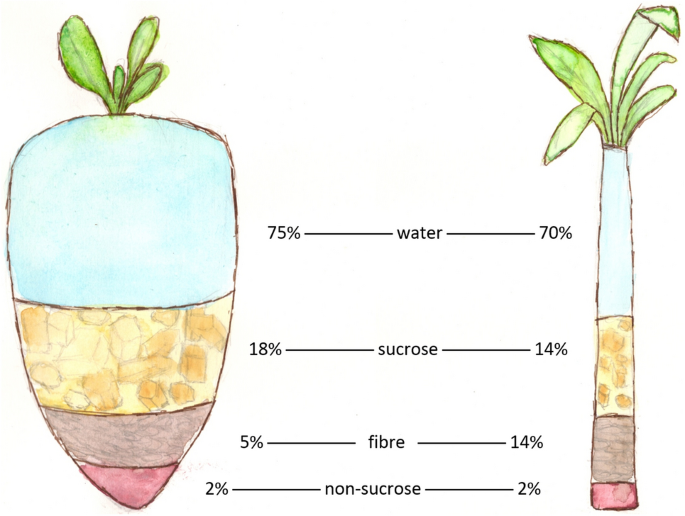
Both crops are rich in sucrose, yet their structure differs somewhat, with sugar cane normally having a higher sugar web content. Each resource also contributes in biofuel manufacturing, with sugar beet usually utilized for ethanol. While both are vital for various applications, their unique growth needs and handling techniques influence their corresponding payments to the sugar market.
Geographic Circulation and Cultivation Conditions
Sugar beet and sugar cane are cultivated in distinctive geographic areas, affected by their particular environment and soil needs. Sugar cane prospers in exotic climates, while sugar beet is much better fit for temperate zones with cooler temperatures. Comprehending these cultivation problems is important for maximizing manufacturing and making sure quality in both plants.
Global Expanding Areas
While both sugar beet and sugar cane are vital resources of sugar, their worldwide expanding regions differ markedly as a result of environment and dirt requirements. Sugar beet grows mainly in warm areas, with significant production focused in Europe, North America, and parts of Asia. These locations typically feature well-drained, productive dirts that support the crop's development cycle. On the other hand, sugar cane is mainly grown in exotic and subtropical regions, with major production hubs situated in Brazil, India, China, and Thailand. This plant flourishes in warm, damp settings that promote its growth. The geographical distribution of these two plants highlights the flexibility of sugar cane to warmer climates, while sugar beet stays dependent on cooler, temperate conditions for peak development.
Environment Requirements
The climate demands for sugar beet and sugar cane vary significantly, showing their adaptation to distinctive ecological problems. Sugar beet thrives in temperate climates, requiring amazing to moderate temperature levels, preferably ranging from 15 ° C to 20 ° C. It is sensitive to frost and gain from well-distributed rains during its expanding period. This plant is typically cultivated in regions such as Europe and North America.
On the other hand, sugar cane flourishes in tropical and subtropical climates, favoring warmer temperatures in between 20 ° C and 30 ° C - Sugar beet vs sugar cane. It calls for bountiful sunlight and constant rainfall, making it appropriate to areas like Brazil, India, and Southeast Asia. The contrasting environment choices of these plants significantly influence their geographic distribution and agricultural methods
Soil Preferences
Although both sugar beet and sugar cane require particular soil problems to grow, their choices vary substantially. Sugar beetroots thrive in well-drained, loamy dirts rich in raw material, with a pH ranging from 6.0 to 7.5. These conditions are generally found in pleasant regions, particularly in Europe and The United States And Canada. On the other hand, sugar cane prefers deep, abundant dirts with superb drain and a somewhat acidic to neutral pH (6.0 to 7.0) This crop is mostly grown in tropical and subtropical climates, such as Brazil, India, and Australia. The geographical circulation of these plants shows their soil choices, as sugar beets are matched for cooler climates, while sugar cane grows in warmer, a lot more humid settings.
Gathering and Handling Techniques
In checking out the harvesting and processing strategies for sugar beet and sugar cane, unique approaches emerge for each and every crop. The comparison of collecting techniques discloses variations in performance and labor requirements, while removal techniques highlight distinctions in the first processing phases. Additionally, recognizing the refining processes is essential for examining the quality and yield of sugar generated from these two sources.
Gathering Methods Contrast
When taking into consideration the gathering approaches for sugar beet and sugar cane, distinct methods arise that reflect the special characteristics of each plant. Sugar beet harvesting normally involves mechanical techniques, utilizing specialized harvesters that uproot the beets from the ground, eliminating tops and soil at the same time. This technique permits for effective collection and decreases plant damages. On the other hand, sugar cane harvesting can be either manual or mechanical. Hands-on harvesting entails employees cutting the stalks close to the ground, while mechanical harvesting makes use of big makers that cut, chop, and gather the cane in one procedure. These distinctions in harvesting techniques highlight the flexibility of each plant to its growing environment and the farming practices widespread in their particular regions.
Extraction Strategies Overview
Removal methods for sugar manufacturing vary considerably in between sugar beet and sugar cane, showing their special attributes and processing needs. Sugar beets are normally harvested making use of mechanical harvesters that cut the roots from the ground, followed by cleaning to get rid of dirt. The beets are after that sliced into slices, known as cossettes, to assist in the extraction of sugar through diffusion or warm water extraction. In contrast, sugar cane is typically gathered by hand or device, with the stalks reduced short. After gathering, sugar cane goes through crushing to draw out juice, which is then clarified and focused. These removal methods highlight the distinct techniques utilized based upon the resource plant's physical features and the wanted effectiveness of sugar extraction.
Refining Procedures Explained
Refining processes for sugar from both sugar beet and sugar cane entail several essential actions that ensure the final item is pure and appropriate for intake. At first, the raw juice extracted from either resource goes through clarification, useful source where contaminations are removed making use of lime and warm. Following this, the juice is evaporated to focus the sugars. For sugar beets, the process often consists of carbonatation, while sugar cane may go through an extra simple formation technique. As soon as concentrated, the syrup goes through formation, creating raw sugar. Ultimately, the raw sugar is purified with centrifugation and more refining, resulting in the white granulated sugar frequently found on store racks. Each step is important in making sure product high quality and security for customers.
Nutritional Profiles and Health Impacts

Health and wellness effects connected with both resources largely stem from their high sugar content. Excessive consumption of sucrose from either source can result in weight gain, dental problems, and enhanced danger of chronic illness such as diabetes mellitus and heart problem. Sugar cane juice, usually eaten in its all-natural type, may provide additional anti-oxidants and phytonutrients contrasted to polished sugar beet products. Ultimately, moderation is essential in using both sugar beet and sugar cane in diet plans to minimize potential health dangers.
Economic Value and Global Manufacturing
The financial significance of sugar beet and sugar cane is significant, because both plants play vital duties in the worldwide farming landscape. Sugar cane, mainly grown in tropical and subtropical areas, represent around 75% of the globe's sugar manufacturing. Countries like Brazil and India are leading manufacturers, adding substantially to their nationwide economic climates with exports and regional consumption.

The worldwide sugar market is valued at billions of bucks, influenced by different factors consisting of climate, trade plans, and customer demand. Accordingly, both sugar beet and sugar cane are important for economic security and development within the farming field worldwide.
Applications in the Food Market
In the food market, sugar beet and sugar cane serve essential roles, offering sweeteners that are integral to a vast range of items. Both sources yield granulated sugar, which is a primary component in baked goods, beverages, and confections. Sugar beet, usually favored in areas with colder climates, is generally found in processed foods such as jams, jellies, and milk items. On the other hand, sugar cane is preferred in tropical areas and is often utilized in beverages like rum and soft beverages.
Beyond granulated sugar, both resources are additionally processed into molasses, syrups, and various other sugar, improving flavor profiles and boosting texture in numerous applications. Additionally, the by-products of sugar production, such as pulp and bagasse, are made use of in developing animal feed and biofuels, further demonstrating their flexibility. Overall, sugar beet and sugar cane are necessary elements of the food sector, affecting taste, texture, and overall item top quality.
Ecological Considerations and Sustainability
As problems regarding environment change and source deficiency expand, the ecological influence of sugar beet and sugar cane cultivation has actually come under examination. Sugar cane, frequently expanded in exotic areas, can bring about logging and environment loss, aggravating biodiversity decline. Furthermore, its farming often depends on extensive water use and chemical plant foods, which can contaminate local waterways.
On the other hand, sugar beet is commonly expanded in warm climates and may advertise dirt health through plant turning. Nonetheless, it likewise deals with challenges such as high water intake and dependence on pesticides.
Both crops add to greenhouse gas discharges during handling, but lasting farming practices are emerging in both markets. These include accuracy agriculture, chemical-free farming, and incorporated insect monitoring. Generally, the ecological sustainability of sugar production continues to be a pressing concern, necessitating continuous assessment and fostering of environment-friendly practices to alleviate adverse impacts on ecosystems and neighborhoods.
Frequently Asked Inquiries
What Are the Distinctions in Taste Between Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane?
The preference differences between sugar beet and sugar cane are refined yet distinct. Sugar beet has a tendency to have a somewhat earthier flavor, while sugar cane provides a sweeter, extra aromatic profile, interesting various cooking preferences.
Can Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Be Made Use Of Interchangeably in Recipes?
Sugar beet and sugar cane can typically be utilized reciprocally in recipes, though subtle distinctions in flavor and appearance may occur. Replacing one for the various other generally preserves the designated sweet taste in cooking applications.

What By-Products Are Developed From Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Handling?
The handling of sugar beets and sugar cane yields numerous by-products. These include molasses, animal feed, and biofuels. Each spin-off serves unique functions, adding to farming and commercial applications past the main sugar extraction.
Exactly How Do Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Affect Dirt Health?
The effect of sugar beet and sugar cane on soil health and wellness varies; sugar beets can boost raw material, while sugar cane might cause dirt deterioration if not handled correctly, impacting nutrient levels and soil structure.
Are There Details Selections of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane?
Numerous certain ranges of sugar beet and sugar cane exist, each adapted check out this site to different climates and soil kinds. These ranges are cultivated for traits such as yield, condition resistance, and sugar web content, enhancing agricultural productivity.